Secured Quantum Services are advanced cybersecurity solutions that use the laws of quantum physics—such as Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)—to protect data and communications from hacking. Unlike traditional encryption, quantum security instantly detects interception attempts, making it ideal for space systems, defense networks, banking, and critical infrastructure.
Introduction
As cyber attacks become more advanced, older encryption techniques may no longer remain secure. The emergence of quantum computers poses a serious risk to today’s cybersecurity systems, including those protecting satellites, financial networks, and national defense infrastructure. Secured quantum services have emerged as a next-generation solution, offering quantum-native security that cannot be silently compromised.
These services are no longer theoretical. With real-world deployments and initiatives in space and defense sectors, quantum security is rapidly becoming a practical necessity.

What Are Secured Quantum Services?
Secured Quantum Services refer to cybersecurity solutions that use quantum mechanics to secure communication, data transfer, and network infrastructure.
Unlike classical security, which relies on mathematical complexity, quantum security is based on physical laws. Any attempt to intercept quantum-secured data immediately alters the system, exposing the attack.
These services include:
- Quantum security services for networks
- Quantum encryption services
- Quantum key distribution services
- Post-quantum security solutions
Why Secured Quantum Services Matter in 2025
Quantum computing is advancing faster than expected. Once fully mature, quantum computers will be able to break many traditional encryption algorithms.
Key risks include:
- Satellite communication interception
- Military and defense data exposure
- Financial transaction compromise
- AI and cloud infrastructure vulnerabilities
Quantum cybersecurity ensures systems remain secure even against future quantum-based attacks.
How Secured Quantum Services Work
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
QKD uses photons to create and share encryption keys. If a hacker attempts to observe or copy the key, the quantum state changes, and the breach is instantly detected.
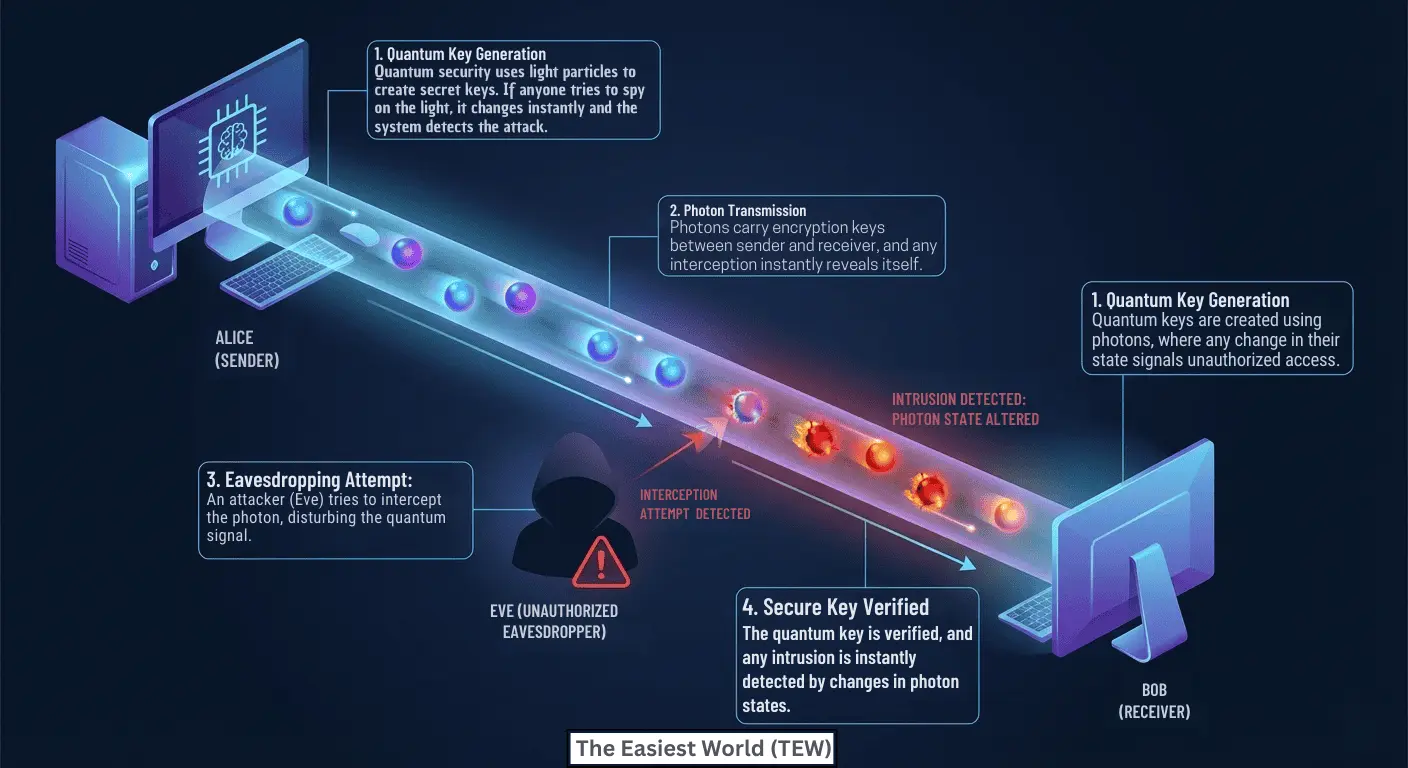
Quantum Encryption
Quantum encryption services ensure that data cannot be copied, intercepted, or altered without detection.
Real-Time Attack Detection
Unlike traditional systems that may detect breaches after damage occurs, quantum systems identify threats during the attack itself.
Types of Secured Quantum Services
Quantum Security Services
These services provide end-to-end protection for networks through the use of quantum-based protocols.
Quantum Encryption Services
Encryption built on quantum physics instead of mathematical assumptions.
Quantum Key Distribution Services
Secure key exchange for terrestrial, orbital, and hybrid networks.
Post-Quantum Security
Encryption designed to resist attacks from quantum computers.
Secured Quantum Services in Space & Defense
Space systems require absolute trust and resilience. Satellite-to-ground communication is highly vulnerable to interception.
Recent real-world initiatives—such as quantum testbeds for space and defense environments—demonstrate how secured quantum services are being operationalized for:
- Satellite communication
- Orbital data transfer
- Defense command networks
- Hybrid earth-space systems
Quantum security is now a strategic requirement, not a future experiment.

Benefits of Secured Quantum Services
- Hack-proof communication
- Immediate intrusion detection
- Protection against quantum computers
- Future-proof security architecture
- Ideal for AI, cloud, space, and defense systems
These benefits make quantum security superior to traditional cybersecurity approaches.
Secured Quantum Services vs Traditional Security
| Feature | Traditional Security | Secured Quantum Services |
|---|---|---|
| Security basis | Mathematical complexity | Quantum physics |
| Hack detection | Often delayed | Instant |
| Quantum-safe | No | Yes |
| Future-proof | Limited | High |
| Copy resistance | No | Yes |
Challenges and Limitations
While powerful, quantum security still faces challenges:
- High deployment cost
- Specialized infrastructure requirements
- Limited global availability
- Need for skilled quantum professionals
However, rapid industry adoption is reducing these barriers.
Future of Secured Quantum Services
The future includes:
- Quantum internet
- Space-based quantum networks
- Global post-quantum standards
- Integration with AI and cloud platforms
As threats evolve, secured quantum services will become the backbone of global cybersecurity.
Conclusion
The design and deployment of digital security undergo a fundamental shift with the introduction of Secured-Quantum-Services. By leveraging the laws of quantum mechanics, these services offer unparalleled protection for data, networks, and communications, especially in space, defense, finance, and critical infrastructure.
As quantum threats become reality, quantum security is no longer optional—it is essential.
Secured quantum services are advanced cybersecurity solutions that use quantum physics, such as quantum key distribution (QKD), to protect data and communications from interception and hacking.
Quantum security works by using quantum states that change when observed. Any interception attempt instantly alters the quantum signal, allowing real-time attack detection.
Secured quantum services cannot be hacked without detection. Any attempt to intercept quantum-secured data immediately reveals the intrusion.
Quantum key distribution is a secure method of sharing encryption keys using photons, ensuring that any eavesdropping attempt is instantly detected.
Post-quantum security is important because it protects systems from future quantum computers that could break traditional encryption methods.
This article has been written with the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) and is being published under the supervision of a professional journalist. The content is provided for informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as professional advice. Readers should independently verify the facts before making decisions based on this information.
References & Sources for Secured Quantum Services
- NSA: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Quantum Cryptography
- Toshiba: Importance of QKD and Post‑Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
- QUDICE: Quantum Security for EU Space Communications
- ETSI: Quantum Key Distribution Services (Use Cases & Examples)
- MDPI: Quantum‑Enhanced Security for Space–Terrestrial Communication Networks
- Financial Times: Secure “Quantum Messages” over Telecom Network

